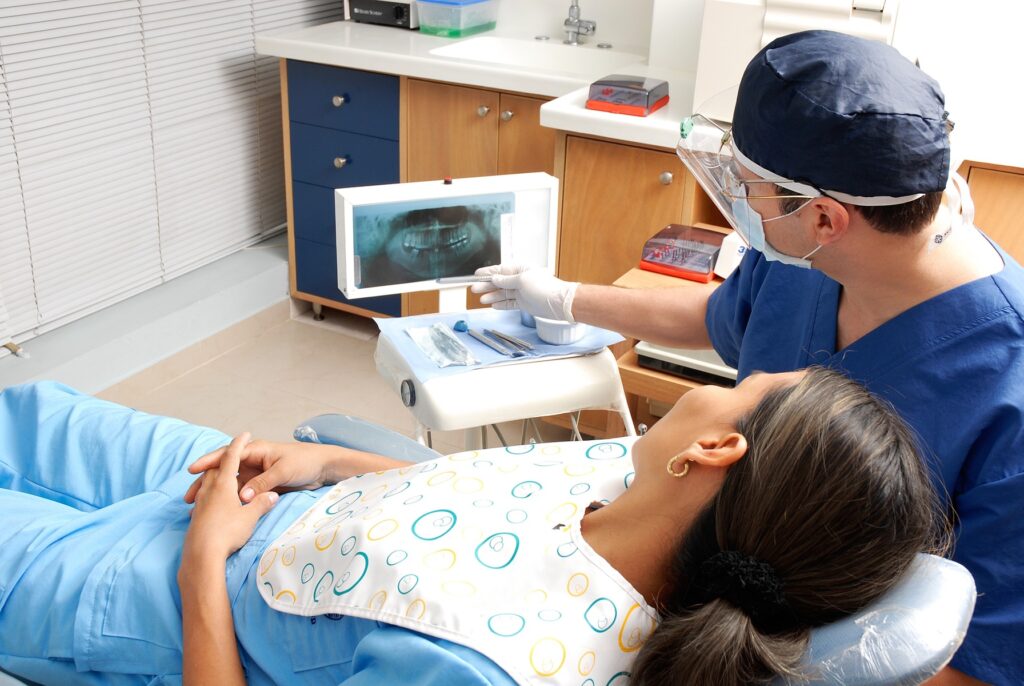
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a common mental health disorder characterized by an extremely short attention span, hyperactivity, and difficulty controlling impulsive behaviors. It is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders in children and is usually diagnosed in childhood and often lasts into adolescence and adulthood. Since people with ADHD often have trouble sitting still for long periods, it can be especially difficult going to the dentist and sitting through long dentist appointments or dental exams, which can cause them to feel anxious and stressed out. Moreover, children with ADHD are often forgetful about brushing their teeth or have trouble carrying out motor skills such as tooth brushing, contributing to poor oral hygiene.
Children with ADHD have a higher prevalence of cavities, tooth decay, and they are more susceptible to traumatic dental injuries. 1Finding a good dental professional can help patients with ADHD feel more comfortable during appointments and also help them develop healthy oral hygiene habits. Furthermore, coordinated efforts by dentists and parents can help create essential support needed by children with ADHD.
This article provides insights on the maintenance of oral health in ADHD patients – its importance and the techniques that can be employed to ensure healthy oral hygiene habits. If you need an emergency dentist near you, get in touch.
Oral Health in ADHD Patients
Children with ADHD have a poor overall oral health status than those without ADHD. Poor oral hygiene habits contribute to a higher prevalence of cavities and dental caries in children with ADHD. The inability to focus, short attention span, and poor motor skills are the reasons for less effective tooth brushing, promoting poor oral health. Moreover, children with ADHD are also more prone to traumatic dental injuries caused by cognitive impairment, motor control impairment, and violent behaviors, which is a common comorbidity of ADHD. Dental traumatic injuries can also affect the psychological well-being of children with ADHD since they may avoid smiling or laughing to avoid showing their teeth, which can bring them shame. 2
Adults with ADHD may have minor physical abnormalities such as a high arched palate caused by orofacial injuries from automobile accidents resulting from their impulsive behavior, inattention, and impaired reaction time. Impulsivity and inattention can also make it difficult for ADHD patients to comply with their oral hygiene home-care regimens, compromising their dental health. Moreover, adults with ADHD may also self-medicate by smoking cigarettes to reduce ADHD symptoms, which can cause oral cancer or periodontal diseases. The frequent consumption of caffeinated beverages in many ADHD patients to improve their cognitive abilities can also harm oral health by staining teeth or producing dental caries if there is too much sugar. 3
The oral health of ADHD patients can also be affected by psychostimulants, commonly used to treat ADHD. Studies have shown that several side effects of psychostimulants threaten the oral and dental care of ADHD patients, including dental erosion and gingival overgrowth. Studies have shown that a low unstimulated salivary flow rate is observed in ADHD patients, which can cause oral health problems such as dental caries, halitosis (bad breath), and plaque accumulation. Furthermore, drugs used for treating ADHD can also cause adverse side effects like xerostomia (sensation of oral dryness/ dry mouth). 4
Complications of Poor Oral Hygiene in ADHD Patients
The above paragraphs clarify that patients with ADHD have poor overall oral health compared to those without it. Therefore, improving the oral hygiene practices in ADHD patients is essential even though it can be challenging. Good oral health habits can help them prevent any serious oral health complications in the future, which may be difficult to cure, require complex medical procedures, and be costly. The following are complications that can be caused by poor oral hygiene practices in ADHD patients
Xerostomia
Xerostomia or dry mouth is a condition where the mouth’s salivary glands do not make enough saliva. Adequate saliva is necessary since it helps moisten and cleanse the mouth, digest food, and control the number of bacteria and fungi in the mouth, preventing infections. Therefore, xerostomia contributes to dental caries, dental diseases, and oral pain. Moreover, xerostomia can also impair chewing ability and decrease taste sensation, diminishing the quality of life. Xerostomia can also impair speech and cause cracks and fissures in the oral mucosa, interfering with people’s social life with xerostomia. Furthermore, xerostomia can also cause sleep disturbances due to the need to wake up and quench the dry mouth. Many medications, including those used for treating ADHD, cause xerostomia. Xerostomia can easily be addressed and treated by dental care professionals.
Dental Trauma
Dental trauma is one of the most serious oral conditions in children and adolescents. Dental complications with traumatic dental injuries may include anterior fractures that cause functional problems and aesthetics issues, tooth discoloration, pulp necrosis, pulp canal obliteration, root resorption, and loss of marginal alveolar bone. Children with ADHD have a higher prevalence of traumatic dental injuries than those without it, mainly due to hyperactivity, impulsivity, and violent behaviors associated with the disorder. 5
Bruxism
Bruxism is the involuntary grinding or clenching of teeth that can occur both while you are awake or asleep. Severe bruxism can lead to damaged teeth, increased tooth pain and sensitivity, worn tooth enamel, jaw disorders, headaches, and other problems. Medications used to treat ADHD cause a higher occurrence of bruxism in ADHD patients. 6
Oral Pain
Poor oral health habits can lead to toothaches, bleeding gums, and gum and jaw aches, which all cause significant oral pain.
Oral Disease
Oral diseases include dental caries, periodontal disease, oral mucosa lesions, and tooth loss.
ADHD patients may have difficulty performing self-care, hurting their oral conditions. ADHD patients also usually consume a high amount of sugar-containing food and beverages and cariogenic foods, contributing to poor oral hygiene. Apart from poor oral health habits, xerostomia caused by ADHD medications also holds a dental caries risk.7
Poor nutrition
Poor oral health habits in ADHD patients, such as lack of tooth brushing, can lead to oral infections and diseases leading to tooth pain and potentially leading to tooth loss, resulting in poor eating behavior and poor nutrition. 8
Coronary Heart Disease
ADHD patients are potentially at risk of developing coronary heart diseases since dental caries and periodontal diseases are hypothesized to contribute to a pro-inflammatory state, accelerating the atherosclerotic process and leading to coronary heart disease.9
Implications for Dental Practice for ADHD Patients
Each ADHD patient needs to be evaluated individually to develop a dental treatment plan since no single plan can work for all patients. Different factors such as the financial situation of the patient, access to care, and other medical problems need to be considered while developing a treatment plan. Furthermore, ADHD patients can be restless, fidgety, or have difficulty sitting in one place for a long period, which can be challenging in dental settings and can interfere with treatment. The following are some implications for dental practice when treating ADHD patients.
Medication
Patients with ADHD usually take medications to treat their disorder. It is important to keep track of the medicines. Stimulants are usually given as treatment for ADHD, and the effects are likely experienced after 30 to 60 minutes. Therefore, clinicians will want to ensure that sufficient time has elapsed between taking the medication and the dental appointment. Moreover, knowing the type of medications is essential since short-acting stimulants can interfere with dental appointments if the dosage is not covered within the dental appointment time. Obtaining the medical history, including the use of illicit substances, is crucial when treating adult ADHD patients to minimize the risk of substance abuse.
Setting the Stage
ADHD patients, especially children with ADHD, do best when they know what to expect during a dental appointment. Therefore, it is essential to communicate with the patient and inform them about what will be accomplished. For children, communication should be done according to the child’s development level so that they understand and remain comfortable during the appointment. Furthermore, discussing incentives that the child can earn if they properly sit through the appointment can help make the experience easier.
Instructions
Inattention and a short attention span are characteristics of ADHD. Therefore, instructions for a dentist appointment should be issued one at a time to ADHD patients so that they are not easily distracted or forget all instructions. Furthermore, instructions to be followed after leaving the dentist’s office should be written down carefully since ADHD patients are usually forgetful and disorganized.
Appointments
Mornings are the best time to schedule dental appointments when ADHD patients are least fatigued, more attentive, and best able to remain seated in the dental chair. Moreover, most medication regimens are designed for the maximum drug effect to occur during the early part of the day, making morning appointments more appropriate. Furthermore, dental professionals should try to make appointments as short as possible since ADHD patients have trouble sitting still for long periods. The waiting times between each patient should also be minimized.
Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement can be useful in obtaining compliance with an ADHD child during appointments. Positive reinforcement can be in terms of praise or tangible rewards such as stickers or temporary tattoos. Positive reinforcement comes from the basic behavioral theory that rewarded behaviors will increase in frequency. Therefore, praising or rewarding the children when they do well will make them more likely to continue good behavior.
Tell-Show-Do Method
The Tell-Show-Do method of behavior has shown value in managing children with ADHD and can be used when introducing new procedures. For example, if dental professionals want children to learn the correct tooth brushing method, they can first tell the child how to do it, then have the child watch them do it, and then allow the child to do it themselves.
Breaks
Breaks are important when working with ADHD patients, even if they are brief. During the break, the clinician can let the patient get out of the dental chair, if possible. Breaks can also be used to let the patient know what will happen during the rest of the appointment or how much longer a procedure will take.
Use of Dental Sedation
Dental sedation may be necessary if ADHD patients need dental work done and cannot cooperate with the dentist. Dental sedation can safely and effectively manage behavior during treatment. The following are the types of dental sedation that can be administered.
- Inhaled minimal sedation – This method involves the patient breathing in nitrous oxide. This mild sedative agent can make the patient relax and safely manage pain and anxiety during dental treatment.
- Oral sedation – This method is the most common in sedation dentistry. During this method, the patient is given a pill to swallow, which can either be mild, making them drowsy, or moderate, making them fall asleep.
- IV moderate sedation – In this method, the sedative drug is given intravenously or through the patient’s vein. This method works quickly, and the dentist can continually adjust the sedation levels.
- Deep sedation – Deep sedation or general anesthesia will make the patient nearly or totally unconscious. With general anesthesia, the patient cannot wake up until the effects wear off or are reversed.
ADHD Medications That May Affect the Oral Health of Patients
ADHD medications come with potential dental-related side effects. The following is a list of medications that affect the oral health of patients with ADHD.
|
Symptom |
Medication |
Side Effects |
|
Generalized |
Amphetamine |
Xerostomia, dysgeusia, bruxism |
|
Atomoxetine |
Xerostomia |
|
|
Hyperactivity |
Antihypertensive (Clonidine, Guanfacine) |
Dysgeusia, sialadenitis dysphagia, xerostomia |
|
Repetitive Behaviors |
Antidepressants (Bupropion, Imipramine) |
Bruxism, glossitis, stomatitis, gingivitis, dysphagia, dysgeusia, sialadenitis, xerostomia, discolored tongue, and oral edema |
Dental Treatment and Prevention
The prevention of oral conditions and diseases is essential in managing the dental health of ADHD patients. Children should be scheduled for early professional dental examinations, and children and adults with ADHD should follow a more frequent dental recall schedule. Furthermore, parents and caregivers of children with ADHD should support them in maintaining healthy daily oral habits such as tooth brushing along with healthy dietary habits. Dental professionals usually follow these guidelines for better treatment and prevention.
- Monitor caries development, bruxism, onset and progression of periodontal disease, and dental or oral trauma carefully.
- Help patients form good oral habits and reinforce oral hygiene.
- Switch to prescription toothpaste. The patients with higher cavity risk may benefit from prescription toothpaste.
- Discourage consumption of sugary foods and beverages.
- If the patient has xerostomia
- Educate them on proper oral hygiene and nutrition.
- Recommend brushing teeth with a fluoride-containing dentifrice before bedtime.
- Recommend lozenges, mints, or gum to stimulate the production of saliva and caries resistance.
The behavior of adults with ADHD in the dental office is usually not significantly different from people without ADHD. Therefore, usually, only minimal modification is required to provide comprehensive dental care to adults receiving ADHD. However, treating children with ADHD can be challenging. The dentists run a child’s appointment smoothly with:
- Understanding their patient needs
- Non-judgmental attitude
- Maintaining their composure
- Positive attitude
- Empathy
- Praise
- Patience
- Directness
Dental Care Tips for Parents of children with ADHD
Below are some tips for parents or caregivers of children with ADHD.
- Take a tour of the dental office before the appointment to familiarize the child with the office and the routine to minimize anxiety levels.
- Talk to the child about visiting the dental office in a positive tone
- Repeat instructions multiple times.
- Use highly stimulating educational material such as pictures or books of the dental office or routine so that the child can visualize what will happen.
- Discuss techniques with dentists on how to create a successful dental visit.
- Maintain a tooth brushing schedule.
- Emphasize regular brushing. The brushing technique will eventually become better with time.
- Be patient with the child and understand that instilling an oral hygiene routine may take time and probably be a trial-and-error method to find a technique that works best.
- Provide them with anticipatory guidance on how to prevent and manage dental injuries.
Finding the Right Dentist for ADHD Patients
Finding the right dentist is essential for the oral health of ADHD patients. Visiting the dentist regularly is important, so it is crucial to find someone who is a good fit, especially for children with ADHD. Parents and caregivers can ask the dentist numerous questions to help them choose the right dentist. The more information they gather, the better it will go. The following questions can help them make the decision.
Do you have experience working with ADHD patients?
Ask the dentist if they have any experience working with ADHD patients since dentists with previous experience will know how to deal with ADHD patients. Furthermore, dentists with previous experience will also be more comfortable ensuring that the dental visit runs smoothly.
Are you comfortable working with an ADHD patient?
ADHD patients require special attention during dental visits, so the dentist must provide them with these. You can also ask the dentist or look for dentists who specialize in special needs care since they have additional years of schooling, which can help them be more accommodating to ADHD patients.
Can any special accommodations be made?
Suitable dentists should be ready to cater to any special accommodations. It is essential for children with ADHD to feel as comfortable as possible during dental appointments, so accommodations like asking whether you can stay with them throughout their appointment can be asked. Moreover, you can also ask the dentist if they can reduce the waiting time between appointments to avoid the child from getting fidgety or hyperactive in the waiting room. Small adjustments like these can make a huge difference to your child’s dental experience.
Conclusion
ADHD patients, especially children with ADHD, are more susceptible to oral diseases such as dental caries due to poor oral hygiene practices. Therefore, regular dental appointments are needed with extra attention to preventative dental care. Children with ADHD also require support from their parents or guardians through frequent monitoring of tooth brushing and good dietary habits to maintain their oral health status. The right dentist will not misinterpret inattention, restlessness, broken appointments, and inability to complete home-care tasks as non-compliance but will view it as a sign of the disorder that requires compassion, understanding, and implementation of special management techniques.
About the author

Dr. Greg Grillo
Dr. Greg Grillo DDS studied at the University of Washington where he received a bachelors degree with Honors and later attended dental school on the same campus. Following school Dr. Greg served in the United States Navy as a dental officer. During this time he received advanced training in specialty areas of dentistry while also treating families of members of the military.
As well as sharing valuable information on dentistry and oral health, Dr. Greg remains a practicing dentist to this day. He works with families in the Okanogan Valley where he lives with his wife and three children.
-
Dr. Greg Grillo#molongui-disabled-link
-
Dr. Greg Grillo#molongui-disabled-link
-
Dr. Greg Grillo#molongui-disabled-link
-
Dr. Greg Grillo#molongui-disabled-link
- Ehlers V, Callaway A, Wantzen S, Patyna M, Deschner J, Azrak B. Oral health of children and adolescents with or without attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) living in residential care in rural Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. BMC Oral Health. 2019;19(1):258. doi:10.1186/s12903-019-0948-5. Available online. Accessed on Aril 23, 2021.
- Sinha S, Praveen P, Prathibha Rani S, Anantharaj A. Pedodontic Considerations in a Child with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Literature Review and a Case Report. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2018;11(3):254-259. doi:10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1522. Available online. Accessed on Aril 23, 2021.
- Friedlander AH, Yagiela JA, Mahler ME, Rubin R. The pathophysiology, medical management and dental implications of adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Am Dent Assoc. 2007;138(4):475-537. doi:10.14219/jada.archive.2007.0199. Available online. Accessed on Aril 23, 2021.
- Hidas A, Noy AF, Birman N, et al. Oral health status, salivary flow rate and salivary quality in children, adolescents and young adults with ADHD. Arch Oral Biol. 2011;56(10):1137-1141. doi:10.1016/j.archoralbio.2011.03.018. Available online. Accessed on Aril 23, 2021.
- Sabuncuoglu O. Traumatic dental injuries and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: is there a link?. Dent Traumatol. 2007;23(3):137-142. doi:10.1111/j.1600-9657.2005.00431. x. Available online. Accessed on Aril 23, 2021.
- Malki GA, Zawawi KH, Melis M, Hughes CV. Prevalence of bruxism in children receiving treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a pilot study. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2004;29(1):63-67. doi:10.17796/jcpd.29.1.3j86338656m83522. Available online. Accessed on Aril 23, 2021.
- Manoharan S, Krishnamoorthy K. Dental Caries and Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)-A Review. J Pharm Sci Res. 2016;8(7):613-615.
- Dursun OB, Şengül F, Esin İS, Demirci T, Yücel N, Ömezli MM. Mind Conduct disorders in children with poor oral hygiene habits and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children with excessive tooth decay. Arch Med Sci. 2016;12(6):1279-1285. doi:10.5114/aoms.2016.59723. Available online. Accessed on Aril 23, 2021.
- Meurman JH, Sanz M, Janket SJ. Oral health, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular disease. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2004;15(6):403-413. Published 2004 Nov 1. doi:10.1177/154411130401500606. Available online. Accessed on Aril 23, 2021.

